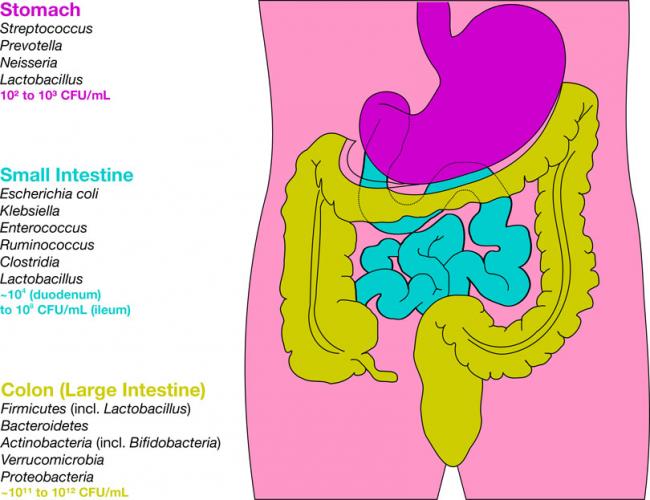
News
- Herbal medicine for Sports
02 Aug 18
- Acupuncture for Dry Eye Syndrome
02 Aug 18
- Vitamin D and Blood Sugar in Women with Osteoporosis
02 Aug 18
- DNA Methylation in ageing and cancer
19 Jun 18
- Topical ozone therapy for herpes zoster
19 Jun 18
- Acupuncture for Anxiety
19 Jun 18
- Vitamin D for Asthma
19 Jun 18
- Soy isoflavones and xenobiotic metabolism
19 Jun 18
- Water exercise for coronary artery disease patients
03 May 18
It is important to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of water-based training programs in order to prescribe it as an alternative in cardiac rehabilitation for patients who have coronary artery disease (CAD) (1). In these patients, autonomic dysfunction is an important physiological change strongly associated with adverse outcomes, morbidity, and mortality. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of water aerobic exercise training (WAET) on the autonomic modulation of heart rate (HR) and body composition, in the rehabilitation of CAD patients. Twenty-six male subjects with CAD were randomly divided into a training group, submitted to the WAET, and a control group. The WAET consisted of 3 weekly sessions on alternate days, totalling 48 sessions. The results showed that only the training group participants had improvement in the HR variability indices; patterns without variation decreased and an increase of patterns of two different variations , Shannon entropy, and normalized conditional entropy, whereas the control group had an increase of 0V (p = .04) and a decrease of normalized conditional entropy. All body composition variables remained unchanged.
References (1) Fiogbe E, et al. Water exercise in coronary artery disease patients, effects on heart rate variability, and body composition: A randomized controlled trial. Physiother Res Int. 2018; doi: 10.1002/pri.1713. - Restless leg syndrome and non-pharmacological treatment: a systematic review
03 May 18
Restless legs syndrome (RLS) is a sensorimotor disorder characterised by an uncomfortable urge to move the legs. This article attempted to synthesise results of non-pharmacological/non-surgical treatment compared to no-treatment controls or alternative treatment for RLS on any relevant outcome (1). The search yielded 442 articles. Eleven trials met inclusion criteria. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, exercise, compression devices, counterstrain manipulation, infrared therapy, and standard acupuncture were significantly more effective for RLS severity than control conditions. Vibration pads, cryotherapy, and transcranial direct current stimulation were ineffective in reducing RLS severity. Vibration pads, cryotherapy, yoga, compression devices, and acupuncture significantly improved some sleep-related outcomes. The authors conclude that repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, exercise, compression devices, counterstrain manipulation, infrared therapy, and standard acupuncture may reduce restless leg syndrome severity. Vibration pads, cryotherapy, yoga, compression devices, and acupuncture may improve some sleep-related outcomes in restless leg syndrome. References (1) Harrison EG, et al. Non-pharmacological interventions for restless legs syndrome: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Disabil Rehabil. 2018; doi: 10.1080/09638288.2018.1453875. - Menstrual disorders and PMS in teenagers and Vitamin D
03 May 18
There have been several studies evaluating the association between vitamin and mineral status and menstrual disturbance (1). In this study, the authors aimed to assess the relationship between the menstrual bleeding pattern and premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, and calcium levels in adolescent girls. There was no significant association between the symptoms of PMS, as assessed by the questionnaire and serum vitamin D status, or serum calcium concentrations, apart from the irritability. There appears to be an association between serum calcium, menstrual blood loss and irritability in adolescent girls. The authors conclude that the level of calcium was associated with the level of menstrual blood loss and irritability. However, no significant association was observed between the menstrual bleeding pattern or the PMS symptoms with a vitamin D status. References (1) Bahrami A, et al. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2018; doi: 10.1080/01443615.2018.1434764. - Nutrients for first-episode psychosis
03 May 18
This article aimed to review all studies examining efficacy, tolerability and the biological mechanisms of action, of nutrient supplementation in first episode psychosis (FEP) (1). A systematic review was conducted. The results included 11 studies. . Six studies examined omega-3 fatty acids, with inconsistent effects on psychiatric symptoms. However, mechanistic studies found significant improvements in hippocampal neuronal health and brain glutathione. Antioxidants "n-acetyl cysteine" and vitamin C also improved oxidative status in FEP, which was associated with reduced psychiatric symptoms. No benefits were found for vitamin E . Finally, one study trialling the amino acid taurine, showed significant improvements in positive symptoms and psychosociall functioning. The authors conclude that there is preliminary evidence that taurine improves outcomes in FEP, whereas effects of omega-3 and antioxidant vitamins/amino-acids are inconsistent; perhaps mainly benefitting patients with high levels of oxidative stress. References (1) Firth J, et al. Adjunctive nutrients in first-episode psychosis: A systematic review of efficacy, tolerability and neurobiological mechanisms. Early Interv Psychiatry. 2018, doi: 10.1111/eip.12544. - Vitamin D effects on athletic performance
03 May 18
This article discusses Vitamin D and its effects on athletic performance (1). Vitamin D is important for calcium homeostasis and bone metabolism. It also has important direct effects on skeletal muscle. Unlike authentic vitamins, which cannot be synthesized in the body, vitamin D is produced in the skin using sunlight. Through its nuclear receptor located throughout the body, including skeletal muscle, vitamin D initiates genomic and nongenomic pathways regulating multiple actions, including muscle cell proliferation and growth. In some studies, vitamin D supplementation has been shown to increase muscle strength, particularly in people who are vitamin D deficient. Higher serum levels of vitamin D are associated with reduced injury rates and improved sports performance. In a subset of the population, vitamin D appears to play a role in muscle strength, injury prevention, and sports performance.
References
1) Abrams GD, et al. Effects of Vitamin D on Skeletal Muscle and Athletic Performance. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-16-00464.
- Use of Complementary Health for acute complaints in the emergency department
20 Apr 18
This study aimed to determine the prevalence of complementary health approaches (CHAs) specifically for acute complaints in patients assessed in a pediatric emergency department (ED) and factors associated with use (1). A cross-sectional survey was offered to patients between the age of 28 days and 18 years assessed at a tertiary pediatric ED. The results showed that of 475 potential participants, 412 (86.7%) participated, of which 369 (89.5%) completed the survey. Overall, 28.7% reported using any CHA for their child to treat the presenting complaint in the prior 72 hours to the ED visit. Gastrointestinal complaints had the highest use of CHA (46.3% of presentations endorsed use). The most common complementary health products used were vitamins and minerals; the most common complementary health practice used was massage. The authors conclude clinicians should consider the use and safety of CHA when evaluating children presenting to the ED with acute conditions.
References
(1) Kalaichandran A, et al. Use of Complementary Health Approaches for Acute Complaints Presenting to the Emergency Department. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2018;doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000001424.
- Reversal agents in the era of non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants
16 Apr 18
The purpose of this review is to outline the currently developed non-vitamin K oral anticoagulant (NOAC) molecular antagonists, their potential clinical roles and future directions (1). The incidence and prevalence of atrial fibrillation (AF) is expected to more than double between 2010 and 2030. Accordingly, the use of NOAC agents for thromboembolic stroke prevention is anticipated to increase. The development of effective and safe antidotes is needed to address the unmet need for rapid anticoagulation reversal. The immediate role for these novel antidotes is for reversal of NOAC activity in life threatening bleeding and urgent surgical intervention. In addition, reversal agents may play an important role in simplifying bridging protocols in the peri-procedural period for catheter ablation of AF and elective surgery. Currently, novel reversal agents are either decoy drug receptors or small molecule non-specific anticoagulant activity inhibitors. The authors discuss how these agents are at various stages of FDA investigation and approval, with emerging prospective data for safety and efficacy.
References
(1) Abed HS, et al. Reversal Agents in the Era of NOACs. J Atr Fibrillation. 2017;10(4):1634.