Related Articles
- 01 Oct 22
A quick look around your local, or online, cosmetics store will easily showcase how popular the emerging realm of clean-and-green skincare products has become. Over time, consumers have become increasingly invested in what ingredients are found or omitted in the skincare products they use.
- 15 Jun 21
Exotic plant oils are a prime example of topical skincare products retaining a deep and rich historical tradition of use across various regions and cultures. Their benefits are now being rediscovered and more firmly established through studies into their cutaneous effects.
- 11 Sep 14
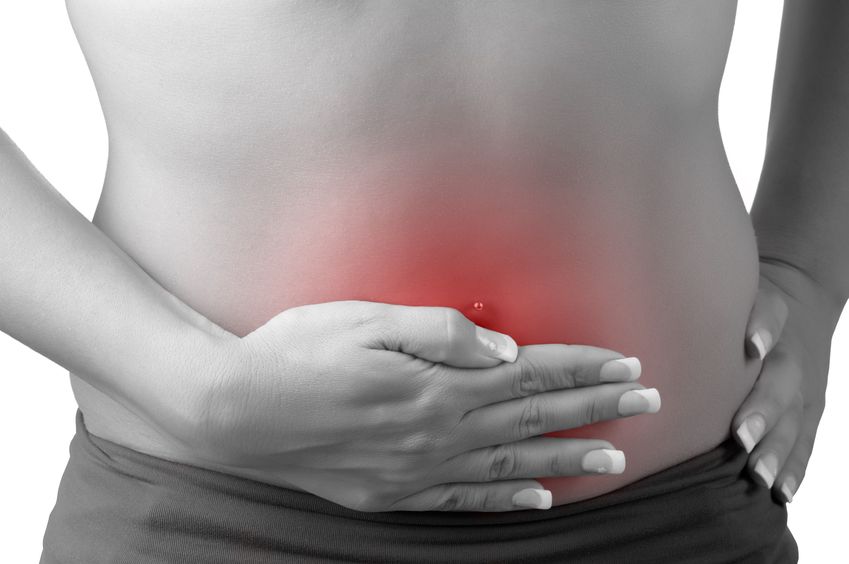
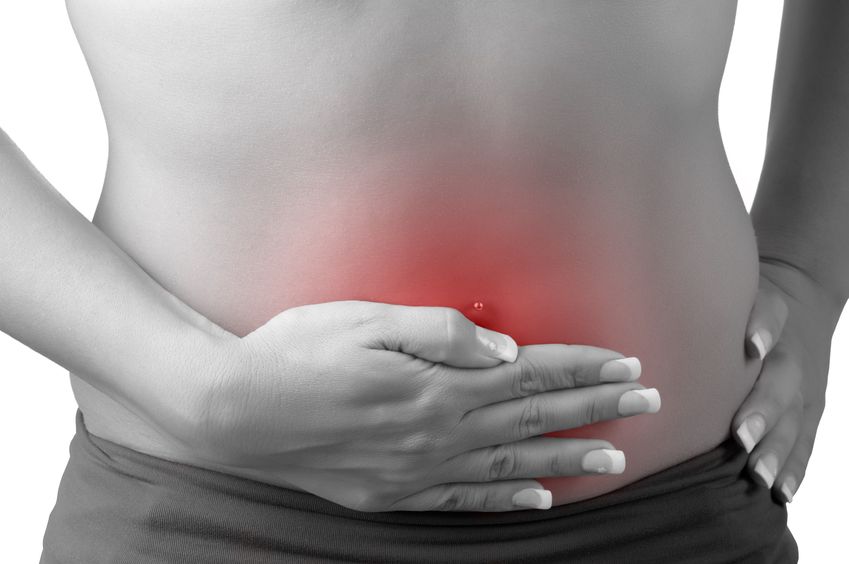 Feeling full quickly when eating, experiencing bloating during and after meals, or suffering from acid reflux may all be signs of low stomach acid – clinically referred to as hypochlorhydria. Hypochlorhydria occurs when the parietal cells in the gastric mucosa do not produce sufficient amounts of hydrochloric acid (HCl). There are numerous underlying causes of parietal dysfunction of psychological, physiological, and infective origin.
Feeling full quickly when eating, experiencing bloating during and after meals, or suffering from acid reflux may all be signs of low stomach acid – clinically referred to as hypochlorhydria. Hypochlorhydria occurs when the parietal cells in the gastric mucosa do not produce sufficient amounts of hydrochloric acid (HCl). There are numerous underlying causes of parietal dysfunction of psychological, physiological, and infective origin. - 07 May 15
 Sunlight has been an integral part of human evolution and the development of life on this planet. Sunlight provides energy to grow plants, providing us with food, shelter and various tools. It is also essential to regulating the seasons. Thus, it has become a necessary component of life as we know it.
Sunlight has been an integral part of human evolution and the development of life on this planet. Sunlight provides energy to grow plants, providing us with food, shelter and various tools. It is also essential to regulating the seasons. Thus, it has become a necessary component of life as we know it. - 03 Jan 22
A variety of natural agents are being explored for their use and applicability in the management of vitiligo, particularly in combination with conventional treatments such as phototherapy. Encompassing dietary, oral supplement, and even topical measures, we will explore a selection of such agents.
- 27 Aug 18
Age-defying serum to reduce wrinkles? Under-eye cream to eradicate puffiness? Deep-cleansing mask to abolish acne? Welcome to the world of cosmeceuticals—a unique and relatively new term it is. Essentially, a cosmeceutical can be any cosmetic product with active, and often naturally derived, ingredients used for a medical, dermatological, or cosmetic purpose.
- 05 Jul 19
The sun rises, you open your eyes, let out a big yawn, and finally decide to get out of bed. Your day has started. Breakfast is consumed… or not (but hopefully has been). E‑mails and social media feeds are all checked. Now it’s finally time to “get ready.” Ladies, before you step out the door, through to the time you go back to sleep, you are estimated to use 12 personal‑care products, containing over 180 ingredients. For the men, you are estimated at 6 personal‑care products containing roughly 85 ingredients.[1]
- 24 Sep 21
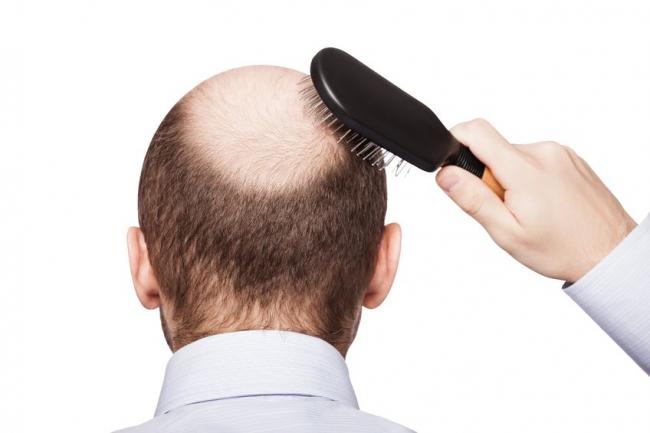
A common concern presenting in general practice is hair loss. Hair is an integral aspect of our identity and feelings of self-esteem, and it offers an element of aesthetic expression for many. To see it recede or thin can be a challenging experience. This article will first review notable information pertaining to the hair physiology, along with key aspects relating to male and female patterns of hair loss (androgenic alopecia).
- 28 Apr 22
A frequent and often frustrating challenge encountered in personal skin-care management is the experience of skin sensitivity. Compounding this situation is the notion of how, despite much recent research being directed toward its exploration, much is left unknown regarding this common cutaneous reaction.
- 02 Jul 14
 Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic and/or relapsing inflammatory skin condition, which often begins in childhood and persists into adulthood. According to the World Allergy Association, the term “atopic” refers to the genetic predisposition to develop an allergic reaction and produce IgE antibodies in response to the exposure to an allergen, usually proteins.
06 Jan 22
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic and/or relapsing inflammatory skin condition, which often begins in childhood and persists into adulthood. According to the World Allergy Association, the term “atopic” refers to the genetic predisposition to develop an allergic reaction and produce IgE antibodies in response to the exposure to an allergen, usually proteins.
06 Jan 22Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) happens when overall bacterial population increases abnormally in the small intestine—especially types of bacteria not commonly found in that part of the digestive tract. Once they reside in the small intestine, they can cause numerous symptoms because they ferment foods like fibres and sugars, which would normally occur in the large intestine.
01 May 21One of the most important topical products to consider in the realm of mitigating the degree of extrinsic photoaging is that of regular sunscreen use.
28 Feb 19Gingerbread, candy canes, festive holidays… snow shovelling, shivering at the bus stop, and dealing with a dead car battery. People tend to fall into two camps, they are either itching for winter, or are frustratingly itching because of winter!
17 Oct 19 Over the last number of years, the topic of acid-base balance has become a very popular health topic. The bulk of the focus has been on dietary means to support the body’s internal acid-base environment, so as to promote a more alkaline (base) milieu. Both diet and supplement measures have been theorized and/or explored for general health and in the management of specific concerns, such as osteoporosis.31 May 19
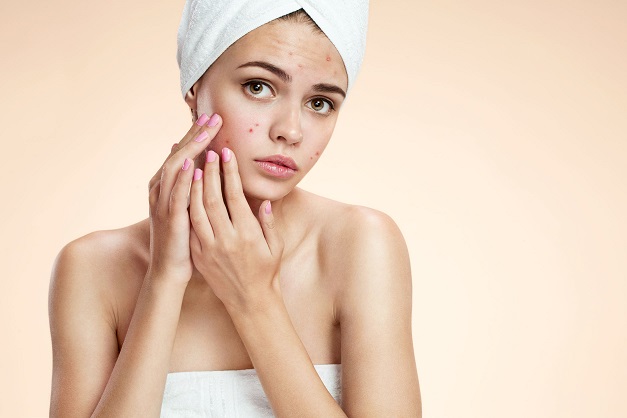
Over the last number of years, the topic of acid-base balance has become a very popular health topic. The bulk of the focus has been on dietary means to support the body’s internal acid-base environment, so as to promote a more alkaline (base) milieu. Both diet and supplement measures have been theorized and/or explored for general health and in the management of specific concerns, such as osteoporosis.31 May 19Acne vulgaris is one of the most common, chronic skin conditions. Up to 80–90% of the population will experience some degree of acne.[1]
27 Aug 18As summer is finally here, I always encourage my patients, friends, and family to spend time outdoors and enjoy the weather while it lasts. Spending time outdoors and in nature has so many positive impacts on our health…
17 May 18A fairly common but often underrecognized condition I encounter as a naturopathic doctor is “chronic yeast infection”; something you may have heard of. It is also sometimes called Candida overgrowth syndrome (COS). This condition can manifest through a variety of mild, systemic, nonspecific symptoms, which may go unexplained and untreated for months or even years at a time for many patients.
01 Dec 22Part 1 of this article introduced us to the various elements composing a typical cosmetic formula, and ingredients often omitted from cleanly produced skincare products. We will now turn our attention to explore the key “life cycle” elements involved in creating a clean skincare product...
01 Dec 13$path = isset($_GET['q']) ? $_GET['q'] : '
';
$link = url($path, array('absolute' => TRUE));$nid = arg(1);
if ($nid == 201312){
?>download pdf
}
?> As baby boomers head into their golden years, research and marketing have followed suit, offering skin-care and food products, as well as more invasive procedures that aim at providing youthful, flawless, glowing skin. As the focus shifts towards maintaining youth both in appearance and on the inside, people are turning to all sorts of treatments in an attempt to look and feel their best.
01 Dec 13
As baby boomers head into their golden years, research and marketing have followed suit, offering skin-care and food products, as well as more invasive procedures that aim at providing youthful, flawless, glowing skin. As the focus shifts towards maintaining youth both in appearance and on the inside, people are turning to all sorts of treatments in an attempt to look and feel their best.
01 Dec 13$path = isset($_GET['q']) ? $_GET['q'] : '
';
$link = url($path, array('absolute' => TRUE));$nid = arg(1);
if ($nid == 201312){
?>download pdf
}
?> Green tea dry leaves from the plant Camellia sinensis, is best known as a component of the traditional Japanese diet, served as small 100 ml cups of tea. Green tea is a rich source of antioxidant flavonoids, in particular the category of flavonoids called catechins. Recently, green tea has received attention for its possible anticancer effects, as well as for more novel uses, including antiviral effects and anti-inflammatory effects.
Green tea dry leaves from the plant Camellia sinensis, is best known as a component of the traditional Japanese diet, served as small 100 ml cups of tea. Green tea is a rich source of antioxidant flavonoids, in particular the category of flavonoids called catechins. Recently, green tea has received attention for its possible anticancer effects, as well as for more novel uses, including antiviral effects and anti-inflammatory effects.
Newsletter
Most Popular
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 01 Jul 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 01 Jul 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 01 Jul 13