Related Articles
- 09 Mar 20
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that is only present during the winter months. This differs from clinical depression, which has no seasonal pattern. SAD also tends to improve when the springtime occurs.
- 17 Dec 19
Sadness, hopelessness and loss of interest in previously interesting activities are the hallmark of a serious, well-known mood disorder commonly referred to as depression. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) defines the disorder based on specific emotions that one must feel for a set amount of time.
- 17 Dec 19
Energy medicine comes in many forms, defined as
anything that works on the energetic biofield of the
human body, also known as the aura. Focusing on
this aspect of health in turn has a ripple effect into
other aspects including emotional, mental, physical,
and even spiritual. I would like to focus this article
specifically on reiki of the Usui origin. - 12 Feb 20
Be honest, how often do you notice and pay attention to your breathing? A couple times a day, once a week, once a month... maybe never? Many of us are doing our best to get healthy by eating plenty of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins sources, and healthy fats as well as exercising, and trying to reduce our stress, but often the same can't be said of breathing.
- 13 Apr 20
Have you met the people that tell you, quite proudly, they never, ever, ever get sick? Do you find yourself feeling just a wee bit jealous? Well, feel jealous no more! Exercising our immune system with a good fever may feel yucky, but it is great for all kinds of reasons.
- 09 Jan 20
In an ever-evolving and modernizing world, we often overlook some of the simplest things. Many cultures are based around certain foods and religious values that teach a way of life. In these cultures, practising these religious values creates a sense of community that binds the group together and further emphasizes the culture. But as families move to new cities and countries, holding on to that cultural upbringing that includes religion becomes harder and harder.
- 09 Jan 20
What is ketosis and the keto diet? Is it good for you, or is it just another lifestyle trend that we’ll forget about in a few years? In this article, we’ll try to answer this question and review the available evidence to see what we can learn.
- 05 May 20
Do you ever question if your health is being helped or hindered by technology? With modern technology advancing, there is a diminished need to leave your home, let alone get off your couch.
- 08 Jul 20
As the COVID-19 pandemic seemed to shut down the world, grocery stores, or at least what was left on the shelves at grocery stores, became an indicator of where people were at in their experience of the stressful event.
- 03 Dec 14
 Our society is always looking for the weight management silver bullet; that magic diet, pill, or fitness machine that will shed excess fat and lead to a fit and firm body. Over the years, a multitude of services and products have hit this multi-billion dollar industry, yet we continue to see obesity rates rise, along with its associated co-morbidities. When it comes to weight management, focusing on the fundamental constituents of healthy living, rather than fads and gimmicks, is always the best bet. However, these common approaches do not always lead to the attainment of desired results.
Our society is always looking for the weight management silver bullet; that magic diet, pill, or fitness machine that will shed excess fat and lead to a fit and firm body. Over the years, a multitude of services and products have hit this multi-billion dollar industry, yet we continue to see obesity rates rise, along with its associated co-morbidities. When it comes to weight management, focusing on the fundamental constituents of healthy living, rather than fads and gimmicks, is always the best bet. However, these common approaches do not always lead to the attainment of desired results. - 05 Jun 17
- 13 Apr 17
- 26 Feb 21
Long before February was declared “Heart Month” in Canada, “American Heart Month” in the United States, and “National Heart Month” in the United Kingdom, children and adults celebrated February 14 as a day of love and affection.
- 17 Jul 16
- 17 Jun 16
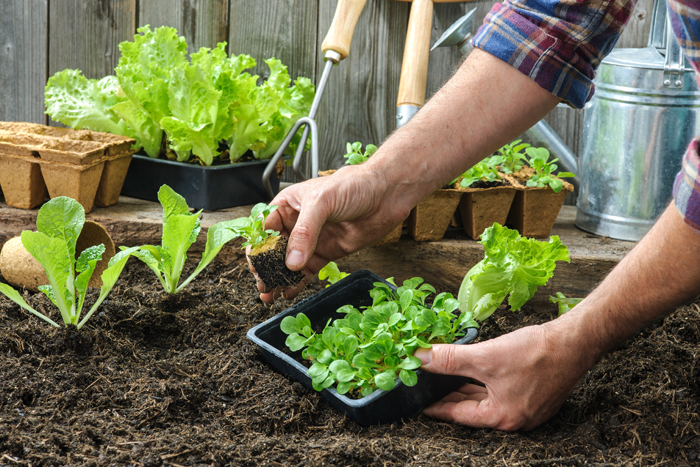 Are you spending enough time outdoors? A recent study found that gardening can be a promising strategy to improve fruit and vegetable consumption, physical activity, and physical function in cancer survivors.[1] When we think about all of the different health habits that could have high return on investment, fruit and vegetable consumption and physical activity are at the top of the list.
Are you spending enough time outdoors? A recent study found that gardening can be a promising strategy to improve fruit and vegetable consumption, physical activity, and physical function in cancer survivors.[1] When we think about all of the different health habits that could have high return on investment, fruit and vegetable consumption and physical activity are at the top of the list. - 02 Sep 15
- 10 Apr 16
 What Is It and What Causes It? Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a form of depression that occurs during certain times of the year. It generally occurs during the colder months, and is associated with shorter days. Reduced sunlight exposure during the fall and winter can disrupt the body’s internal clock, also known as the circadian rhythm.
What Is It and What Causes It? Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a form of depression that occurs during certain times of the year. It generally occurs during the colder months, and is associated with shorter days. Reduced sunlight exposure during the fall and winter can disrupt the body’s internal clock, also known as the circadian rhythm. - 09 Jul 15
 Whole-body cryotherapy (WBC) is a health promoting treatment that involves short exposures to air temperatures below −100°C [1]. WBC treatments last approximately 2-5 minutes and the frequency of treatments can vary based on the purpose of use. The patient is placed in a small cabin that emits a dry cold mist that is suctioned from a neighbouring liquid nitrogen tank.
Whole-body cryotherapy (WBC) is a health promoting treatment that involves short exposures to air temperatures below −100°C [1]. WBC treatments last approximately 2-5 minutes and the frequency of treatments can vary based on the purpose of use. The patient is placed in a small cabin that emits a dry cold mist that is suctioned from a neighbouring liquid nitrogen tank. - 11 Mar 16
- 22 Dec 16
Newsletter
Most Popular
- 26 Sep 13
- 11 Aug 15
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 01 Jul 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 01 Jul 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 01 Jul 13