[1] Teras, L.R., A.V. Patel, M. Wang, S.‑S. Yaun, K. Anderson, R. Brathwaite, B.J. Caan, et al. “Sustained weight loss and risk of breast cancer in women ≥50 years: a pooled analysis of prospective data.” Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 2019; DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djz226
[2] Sampson, M., A. Clark, M. Bachmann, N. Garner, L. Irvine, A. Howe, C. Greaves, et al. “Lifestyle intervention with or without lay volunteers to prevent type 2 diabetes in people with impaired fasting glucose and/or nondiabetic hyperglycemia: A randomized clinical trial.” JAMA Internal Medicine, Vol. 181, No. 2 (2021): 168–178.
[3] Lavie, C.J., R.V. Milani, and H.O. Ventura. “Obesity and cardiovascular disease: Risk factor, paradox, and impact of weight loss.” Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Vol. 53, No. 21 (2009): 1925–1932.
[4] Swencionis, C., J. Wylie‑Rosett, M.R. Lent, M. Ginsberg, C. Cimino, S. Wassertheil‑Smoller, A. Caban, and C.‑J. Segal‑Isaacson. “Weight change, psychological well-being, and vitality in adults participating in a cognitive—Behavioral weight loss program.” Health Psychology, Vol. 32, No. 4 (2013): 439–446.
[5] Mazidi, M., N. Katsiki, D.P. Mikhailidis, N. Sattar, and M. Banach. “Low-carbohydrate diets and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: A population-based cohort study and pooling prospective studies.” European Heart Journal, Vol. 40, No. 34 (2019) :2870–2879.
[6] Hursel, R., W. Viechtbauer, and M.S. Westerterp‑Plantenga. “The effects of green tea on weight loss and weight maintenance: A meta-analysis.” International Journal of Obesity, Vol. 33, No. 9 (2009): 956–961.
[7] Hartley, L., N. Flowers, J. Holmes, A. Clarke, S. Stranges, L. Hooper, and K. Rees. “Green and black tea for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease.” The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Vol. 2013, No. 6 (2013): CD009934.
[8] Kelly, K.P., O.P. McGuinness, M. Buchowski, J.J. Hughey, H. Chen, J. Powers, T. Page, and C.H. Johnson. “Eating breakfast and avoiding late-evening snacking sustains lipid oxidation.” PLOS Biology, Vol. 18, No. 2 (2020): e3000622.
[9] Byrne, N.M., A. Sainsbury, N.A. King, A.P. Hills, and R.E. Wood. “Intermittent energy restriction improves weight loss efficiency in obese men—The MATADOR study.” International Journal of Obesity, Vol. 42, No. 2 (2018): 129–138.
[10] Hollis, J.F., C.M. Gullion, V.J. Stevens, P.J. Brantley, L.J. Appel, J.D. Ard, C.M. Champagne, et al., Weight Loss Maintenance Trial Research Group. “Weight loss during the intensive intervention phase of the weight-loss maintenance trial.” American Journal of Preventive Medicine, Vol. 35, No. 2 (2008): 118–126.
[11] Lennerz, B.S., D.C. Alsop, L.M. Holsen, E. Stern, R. Cojas, C.B. Ebbeling, J.M. Goldstein, and D.S. Ludwig. “Effects of dietary glycemic index on brain regions related to reward and craving in men.” The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Vol. 98, No. 3 (2013): 641–647.
[12] Harrold, J.A., G. Hughes, E.J. Boyland, N.J. Williams, R. McGill, J.E. Blundell, G. Finlayson, et al. “Dried fruit (prune) consumption does not undermine active weight management or produce adverse gastrointestinal effects.” International Nut and Dried Fruit Council, https://www.nutfruit.org/health-professionals/health-research/dried-fruit-prune-consumption-does-not-undermine-active-weight-management-or-produce-ad…, consulted 2021‑02‑22.
[13] Cangiano, C., A. Laviano, M. Del Ben, I. Preziosa, F. Angelico, A. Cascino, and F. Rossi‑Fanelli. “Effects of oral 5‑hydroxy-tryptophan on energy intake and macronutrient selection in non-insulin dependent diabetic patients.” International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders, Vol. 22, No. 7 (1998): 648–654.
[14] Jiang, J., M.P. Emont, H. Jun, X. Qiao, J. Liao, D.‑I. Kim, and J. Wu. “Cinnamaldehyde induces fat cell-autonomous thermogenesis and metabolic reprogramming.” Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, Vol. 77 (2017): 58–64.
[15] Dulloo, A.G., C. Duret, D. Rohrer, L. Girardier, N. Mensi, M. Fathi, P. Chantre, and J. Vandermander. “Efficacy of a green tea extract rich in catechin polyphenols and caffeine in increasing 24-h energy expenditure and fat oxidation in humans.” The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Vol. 70, No. 6 (1999): 1040–1045.
[16] Dulloo, Duret, Rohrer, Girardier, Mensi, Fathi, Chantre, and Vandermander. “Efficacy of a green tea extract.”
[17] Sanchez, M., C. Darimont, V. Drapeau, S. Emazy‑Adar, M. Lepage, E. Rezzonico, C. Ngom‑Bru, et al. “Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus CGMCC1.3724 supplementation on weight loss and maintenance in obese men and women.” The British Journal of Nutrition, Vol. 111, No. 8 (2014): 1507–1519.
[18] Yang, C., L. Li, L. Yang, H. Lǚ, S. Wang, and G. Sun. “Anti-obesity and hypolipidemic effects of garlic oil and onion oil in rats fed a high-fat diet.” Nutrition & Metabolism, Vol. 15 (2018): 43.
[19] Soleimani, D., Z. Paknahad, G. Askari, B. Iraj, and A. Feizi. “Effect of garlic powder consumption on body composition in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.” Advanced Biomedical Research, Vol. 5 (2016): 2.
 Our society is always looking for the weight management silver bullet; that magic diet, pill, or fitness machine that will shed excess fat and lead to a fit and firm body. Over the years, a multitude of services and products have hit this multi-billion dollar industry, yet we continue to see obesity rates rise, along with its associated co-morbidities. When it comes to weight management, focusing on the fundamental constituents of healthy living, rather than fads and gimmicks, is always the best bet. However, these common approaches do not always lead to the attainment of desired results.
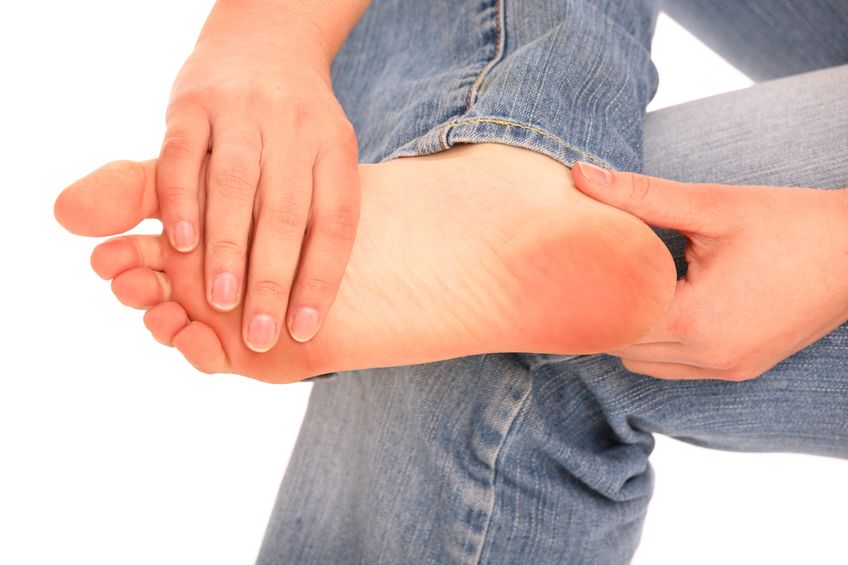
Our society is always looking for the weight management silver bullet; that magic diet, pill, or fitness machine that will shed excess fat and lead to a fit and firm body. Over the years, a multitude of services and products have hit this multi-billion dollar industry, yet we continue to see obesity rates rise, along with its associated co-morbidities. When it comes to weight management, focusing on the fundamental constituents of healthy living, rather than fads and gimmicks, is always the best bet. However, these common approaches do not always lead to the attainment of desired results. Gout is a severely painful inflammatory joint condition that most commonly affects the large toe, and (more rarely) the knee. Up to 4% of western populations are affected, making this the most common inflammatory arthritis. Gout attacks are acutely painful, and although they resolve rapidly on treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs, they may recur frequently; up to 60% of patients with gout will have recurrent attacks within one year or suffer from chronic gout.
Gout is a severely painful inflammatory joint condition that most commonly affects the large toe, and (more rarely) the knee. Up to 4% of western populations are affected, making this the most common inflammatory arthritis. Gout attacks are acutely painful, and although they resolve rapidly on treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs, they may recur frequently; up to 60% of patients with gout will have recurrent attacks within one year or suffer from chronic gout.