Related Articles
- 12 Feb 20
Be honest, how often do you notice and pay attention to your breathing? A couple times a day, once a week, once a month... maybe never? Many of us are doing our best to get healthy by eating plenty of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins sources, and healthy fats as well as exercising, and trying to reduce our stress, but often the same can't be said of breathing.
- 12 Feb 20
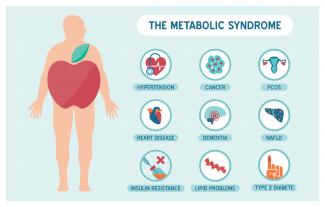
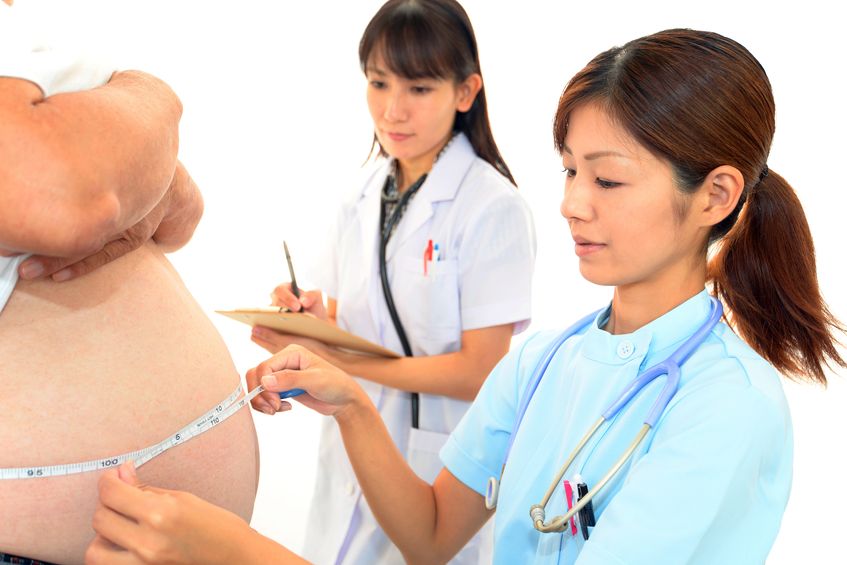
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of risk factors that increase one’s chances of developing serious illnesses in the future. Metabolic syndrome doubles the chance of developing cardiovascular disease while increasing the risk of diabetes, fatty liver, and several types of cancers.[1][2]
- 13 Apr 20
Have you met the people that tell you, quite proudly, they never, ever, ever get sick? Do you find yourself feeling just a wee bit jealous? Well, feel jealous no more! Exercising our immune system with a good fever may feel yucky, but it is great for all kinds of reasons.
- 10 Jun 20
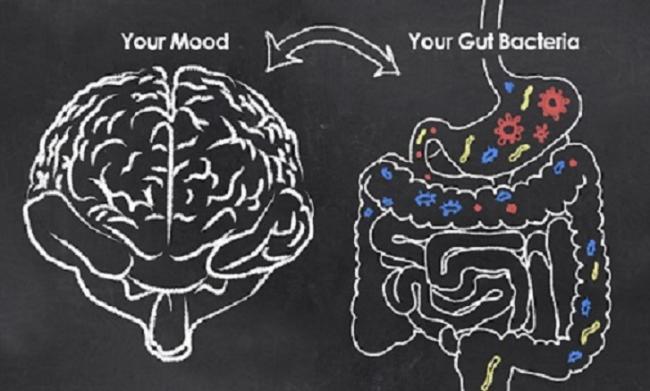
By now, most of us have heard the word microbiome—the collection of trillions of functional bacteria of all different species found in many places throughout our bodies, such as our skin, gut, mouth, vagina, and lungs.
- 08 Jul 20
With pregnancy come major changes in circulation. It’s no wonder: With an increase in body weight from the fetus and surrounding fluid, extra pressure is added onto organs and other structures like the weaker-walled veins. The body’s blood volume also increases and these changes can result in swelling, varicose veins, and hemorrhoids.
- 01 Feb 14
$path = isset($_GET['q']) ? $_GET['q'] : '
';
$link = url($path, array('absolute' => TRUE));$nid = arg(1);
if ($nid == 201402){
?>download pdf
}
?> Many readers will be aware of an ongoing public debate regarding the validity of naturopathic medicine. The debate often centers on the existence of evidence to support the safety and effectiveness of naturopathic medicine. In this article, we throw new light on the state of naturopathic medicine research and highlight the oft-overlooked body of evidence that already exists.
17 Dec 19
Many readers will be aware of an ongoing public debate regarding the validity of naturopathic medicine. The debate often centers on the existence of evidence to support the safety and effectiveness of naturopathic medicine. In this article, we throw new light on the state of naturopathic medicine research and highlight the oft-overlooked body of evidence that already exists.
17 Dec 19Collagen peptides have seemingly appeared out of nowhere. They are being advertised on social media, can be found on the covers of magazines… even my hairdresser has been talking about how she adds collagen peptides to her smoothie! But what are collagen peptides? Why is everyone adding this powder to their coffee, smoothies, or breakfast oatmeal bowl? And the real question is: Should you be adding collagen peptides to your diet as well?
13 Apr 15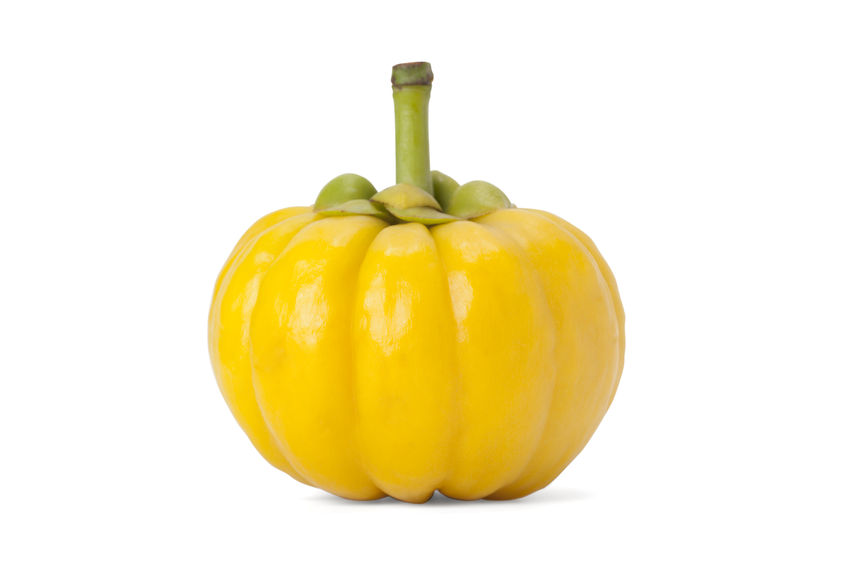 The prevalence of overweight and obesity has skyrocketed in North America over recent years, and weight management strategies employed have had little widespread success. Both science and the public have been interested in natural and synthetic weight loss aids for decades, the most recent slimming agent being Garcinia cambogia (G. cambogia) and its extract (−)‑hydroxycitric acid (HCA).26 Feb 21
The prevalence of overweight and obesity has skyrocketed in North America over recent years, and weight management strategies employed have had little widespread success. Both science and the public have been interested in natural and synthetic weight loss aids for decades, the most recent slimming agent being Garcinia cambogia (G. cambogia) and its extract (−)‑hydroxycitric acid (HCA).26 Feb 21Long before February was declared “Heart Month” in Canada, “American Heart Month” in the United States, and “National Heart Month” in the United Kingdom, children and adults celebrated February 14 as a day of love and affection.
18 Jan 19To begin discussing this topic, we should first review the mechanisms behind developing CVD, so that we can discuss ways to prevent it as well as reverse it once an individual has developed it. As mentioned previously, the development of CVD begins with atherosclerosis. This is the term used by medical professionals to describe the process of plaque (fat, cholesterol, etc.) formation and the subsequent hardening of the walls of the arteries.
17 Jul 1605 Jul 1922 Dec 15 According to Statistics Canada, results from the 2009 to 2011 Canadian Health Measures Survey (CHMS) indicate that 1 in 5 Canadian adults aged 18 to 79 had metabolic syndrome. Metabolic Syndrome, also known as Syndrome X, Insulin Resistance Syndrome, or Mets refers to a cluster of conditions that occur together. These conditions include high blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, excess body fat around the waist or mid-central obesity, and abnormal cholesterol levels. 08 Jun 15
According to Statistics Canada, results from the 2009 to 2011 Canadian Health Measures Survey (CHMS) indicate that 1 in 5 Canadian adults aged 18 to 79 had metabolic syndrome. Metabolic Syndrome, also known as Syndrome X, Insulin Resistance Syndrome, or Mets refers to a cluster of conditions that occur together. These conditions include high blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, excess body fat around the waist or mid-central obesity, and abnormal cholesterol levels. 08 Jun 15 Niacin is one form of vitamin B3. Niacinamide and inositol hexanicotinate are the other two forms of B3 that exist; these forms are generally used to treat different conditions within the body. B vitamins ultimately help the body utilize fats and proteins; they also help convert food into fuel which is then used to produce energy.13 Feb 16
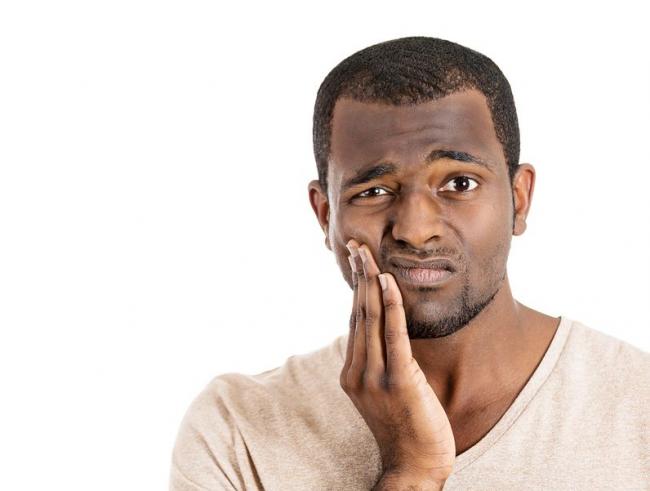
Niacin is one form of vitamin B3. Niacinamide and inositol hexanicotinate are the other two forms of B3 that exist; these forms are generally used to treat different conditions within the body. B vitamins ultimately help the body utilize fats and proteins; they also help convert food into fuel which is then used to produce energy.13 Feb 16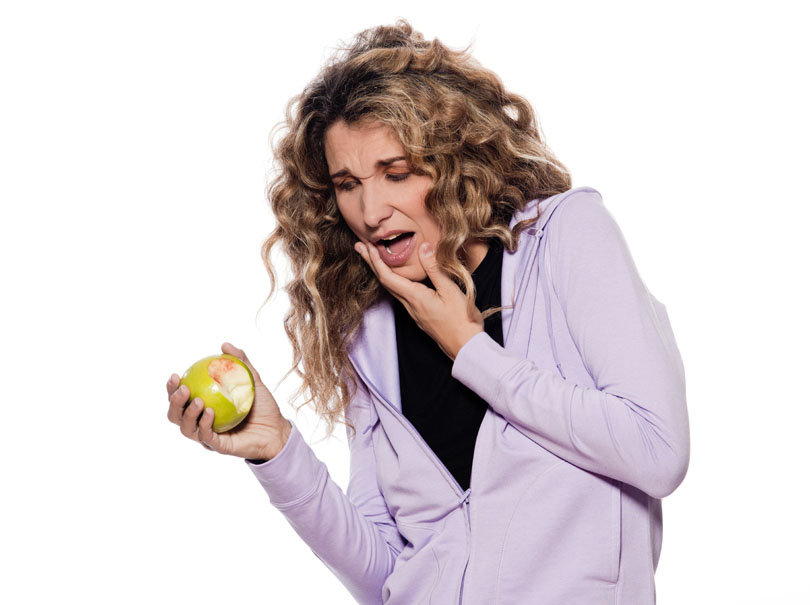 Noticing blood while brushing or flossing can be alarming and shouldn’t be ignored! The importance of oral health is a concept introduced to most Canadians at a very young age, and with good reason. The Ontario Dental Hygienist’s Association reports that the link between oral infections and other diseases in the body is becoming well-documented and accepted within the health-care community. Periodontal disease is one of the most common human diseases13 Apr 15
Noticing blood while brushing or flossing can be alarming and shouldn’t be ignored! The importance of oral health is a concept introduced to most Canadians at a very young age, and with good reason. The Ontario Dental Hygienist’s Association reports that the link between oral infections and other diseases in the body is becoming well-documented and accepted within the health-care community. Periodontal disease is one of the most common human diseases13 Apr 15 Pre-eclampsia is a condition that has life-threatening consequences if not treated immediately. If you are a pregnant woman experiencing symptoms of pre-eclampsia, it is important to seek medical attention. Although the cause remains unknown, advancements in research are being made, and several theories exist for the cause of the condition.09 Mar 15
Pre-eclampsia is a condition that has life-threatening consequences if not treated immediately. If you are a pregnant woman experiencing symptoms of pre-eclampsia, it is important to seek medical attention. Although the cause remains unknown, advancements in research are being made, and several theories exist for the cause of the condition.09 Mar 15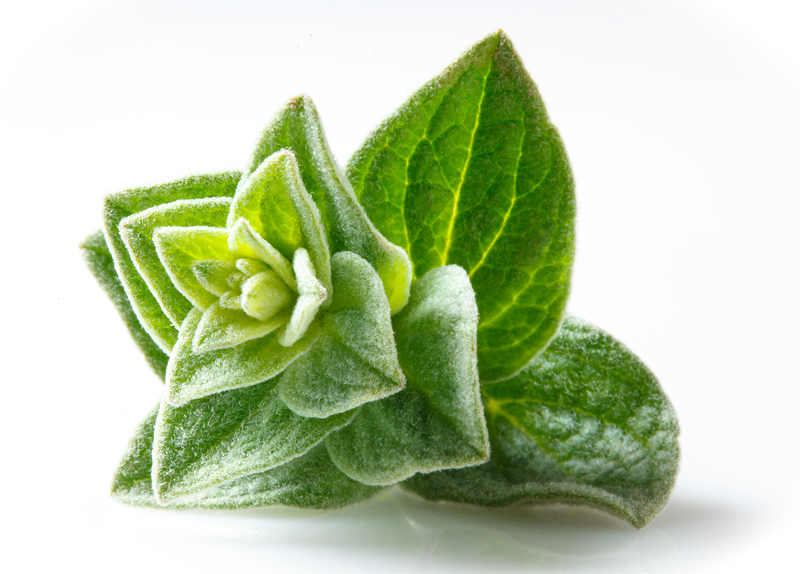 Origanum vulgare (the scientific name of oregano) has been studied in depth due to a number of interesting and exciting potential clinical uses. There is also an ongoing interest in a number of industries to replace synthetic chemicals with natural products that have similar properties. Many bioactive compounds can be found in aromatic plants, and there are a number of different ways they can be extracted.13 Apr 15
Origanum vulgare (the scientific name of oregano) has been studied in depth due to a number of interesting and exciting potential clinical uses. There is also an ongoing interest in a number of industries to replace synthetic chemicals with natural products that have similar properties. Many bioactive compounds can be found in aromatic plants, and there are a number of different ways they can be extracted.13 Apr 15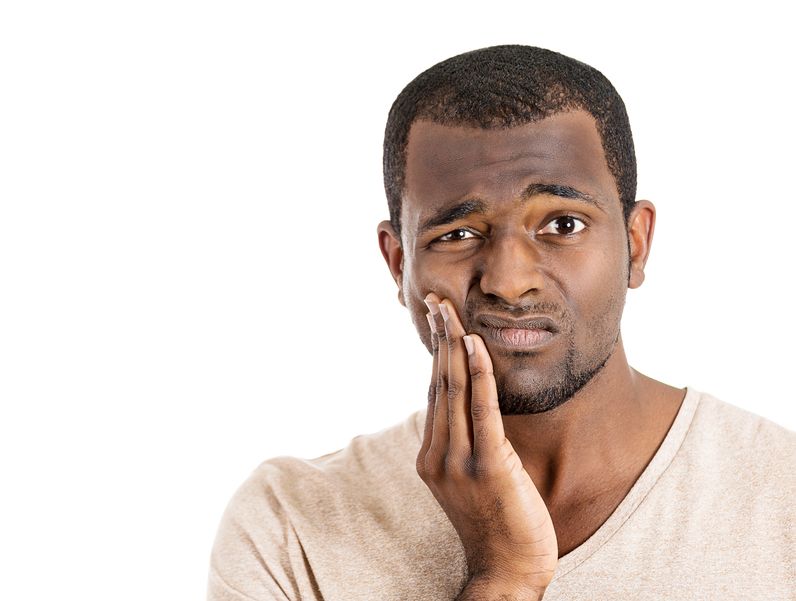 Periodontitis is the result of gingivitis progressing to a more serious stage. It is characterized by swollen, reddish, and bleeding gums, as well as bad breath. Severe periodontitis affects 10–15% of adults, while moderate periodontitis affects 40–60% of adults. Despite its high prevalence, it is largely unrepresented as a chronic inflammatory disease.17 Jun 1606 Sep 16
Periodontitis is the result of gingivitis progressing to a more serious stage. It is characterized by swollen, reddish, and bleeding gums, as well as bad breath. Severe periodontitis affects 10–15% of adults, while moderate periodontitis affects 40–60% of adults. Despite its high prevalence, it is largely unrepresented as a chronic inflammatory disease.17 Jun 1606 Sep 16
Newsletter
Most Popular
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 01 Jul 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 01 Jul 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 17 Jun 13
- 01 Jul 13